
In the field of machine vision inspection, the precise focusing capability of autofocus microscopes directly impacts imaging quality and inspection efficiency. The POMEAS motorized zoom autofocus video microscope offers flexible solutions for diverse scenarios through three core focusing modes—autofocus, one-touch focus, and manual focus—combined with four-zone light adjustment technology.
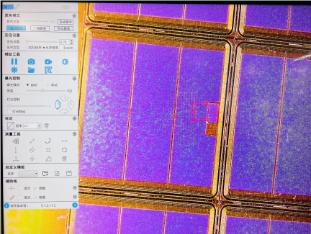

Autofocus: The Smart Choice for Dynamic Scenes
Autofocus (AF) operates based on contrast detection or phase detection principles. The system analyzes contrast gradients in image regions in real time, driving motors to rapidly adjust lens position until the target area achieves maximum contrast. This process typically completes within milliseconds, making it suitable for scenarios like dynamic object detection and continuous sample scanning.
For example: In semiconductor chip inspection, autofocus accommodates micrometer-level height variations on wafer surfaces, ensuring clear imaging at every inspection point. Its core advantage lies in “zero manual intervention” intelligence, though environmental light interference may affect contrast calculation accuracy.
One-Touch Focus: A Quick Solution for Efficient Scenes
One-Click Focus Mode achieves rapid focusing through preset parameters. Users simply trigger the button, and the system recalls stored focus positions or algorithm models to jump directly to the target focal plane. This mode is ideal for scenarios involving fixed samples and repetitive inspection processes.
For example: During PCB board inspection, operators can apply One-Touch Focus in bulk for identical product models, significantly reducing individual inspection times. Compared to Auto Focus, One-Touch Focus sacrifices some environmental adaptability but gains higher operational efficiency and stability, making it particularly suitable for rapid quality control on standardized production lines.
Manual Focus: Fine-Tuned Precision Control
Manual focus enables precise adjustment of the focal plane through physical knobs or software interfaces, achieving sub-micron accuracy down to 0.1 micrometers. This mode is ideal for scenarios demanding ultimate imaging detail.
For example: In biomedical research, observing organelle structures requires manual fine-tuning to capture subcellular-level details. This mode grants users maximum control but demands operational experience to avoid over- or under-adjustment. When paired with four-zone light source adjustment, manual focus can synergize with localized illumination optimization to further enhance image signal-to-noise ratio.
Product recommendation
TECHNICAL SOLUTION
MORE+You may also be interested in the following information
FREE CONSULTING SERVICE
Let’s help you to find the right solution for your project!

- APPICATION CASE
- RESOURCE CENTER
- DOWNLOAD CENTER
SOLUTIONS SUPPORT
- ZOOM LENS SELECTION TOOL
- TELECENTRIC LENS SELECTION TOOL
- FA LENS SELECTION TOOL
- ZOOM RATIO TABLE
- CERTIFIED MODEL
SELECTION TOOL
- WHY POMEAS
- FAQ
- PRIVACY POLICY
- TERMS OF USE
- DELIVERY & RETURN POLICY
CUSTOMER CARE
 ADDRESS
ADDRESS
Add.:No.68, Chongwei Road, Baizhoubian, East district, Dongguan, China, 523000
CONTACT
 Tel:+ 86-0769-2266 0867
Tel:+ 86-0769-2266 0867
 Fax:+ 86-0769-2266 0867
Fax:+ 86-0769-2266 0867
 E-mail:marketing@pomeas.com
E-mail:marketing@pomeas.com

Wechat QR code

 ASK POMEAS
ASK POMEAS  PRICE INQUIRY
PRICE INQUIRY  REQUEST DEMO/TEST
REQUEST DEMO/TEST  FREE TRIAL UNIT
FREE TRIAL UNIT  ACCURATE SELECTION
ACCURATE SELECTION 