What you need to know about industrial telecentric lens selection?
In the field of industrial automation production and quality inspection, the application of machine vision systems is becoming more and more widespread, and industrial telecentric lenses, as the “eyes” of machine vision, the accuracy of their selection directly affects the accuracy and reliability of the inspection results. However, in the actual selection process, many engineers and practitioners tend to ignore some key inspection needs. Understand these needs in order to find the most appropriate industrial telecentric lens with the machine vision program, the next step is to discuss in depth in the selection of telecentric lens is often overlooked a few key points.


A、Fitness for Test Objects
1. The size of the measured object: Whether it is micron-level electronic components or automotive parts, different sizes of objects need to match different specifications of the lens.

For example, the detection of tiny chips, you need to choose a telecentric lens with high resolution and a small field of view to ensure that the details on the chip can be clearly captured; while for larger sized mechanical parts, it is necessary to consider the field of view of the lens can completely cover the surface of the part.
2. Material and surface characteristics: metal, plastic, glass and other different materials of the object, the light reflection and refraction characteristics are different. Smooth surface metal workpiece, may produce glare due to reflection, affecting the quality of imaging, at this time you need to choose anti-glare ability of telecentric lens; and for transparent or translucent material objects.


Such as glass, plastic film, etc., to focus on whether the depth of field of the lens is sufficient to clearly present the internal structure of the object or multi-layer surface features. In addition, the color of the object will also affect the imaging effect, for objects with similar colors and low contrast, the lens needs to have good color reproduction ability and gray scale processing ability to distinguish between different areas.
B、Working Distance
1. Working distance refers to the distance from the front of the lens to the surface of the object to be measured. The appropriate working distance not only ensures that the lens to obtain a clear image, but also for the entire inspection system to reserve enough operating space to avoid collision between the lens and the object. In some automated production lines, robotic arms or conveyor devices will drive the object under test to move, if the working distance is too short, the lens may be object or mechanical structure touched, resulting in damage; working distance is too long, it may introduce more environmental interference, affecting the quality of the image.
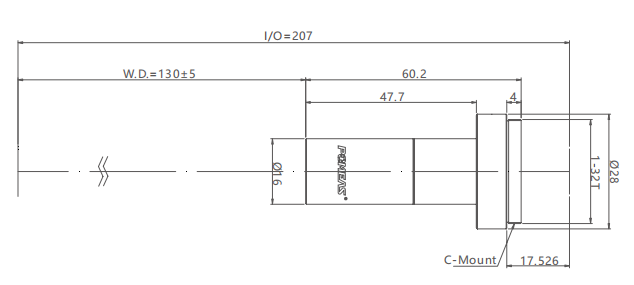
For example, in the precision assembly link, may need to be in close proximity to the parts of high-precision detection, then you need to choose a shorter working distance, higher magnification telecentric lens; and for the appearance of some large objects detection, in order to ensure the safety and ease of operation, it may require a longer working distance, you should choose the appropriate specifications of the lens. At the same time, but also consider the working distance on the lens focal length, depth of field and other parameters to ensure that the working distance, the lens can meet the requirements of detection accuracy.

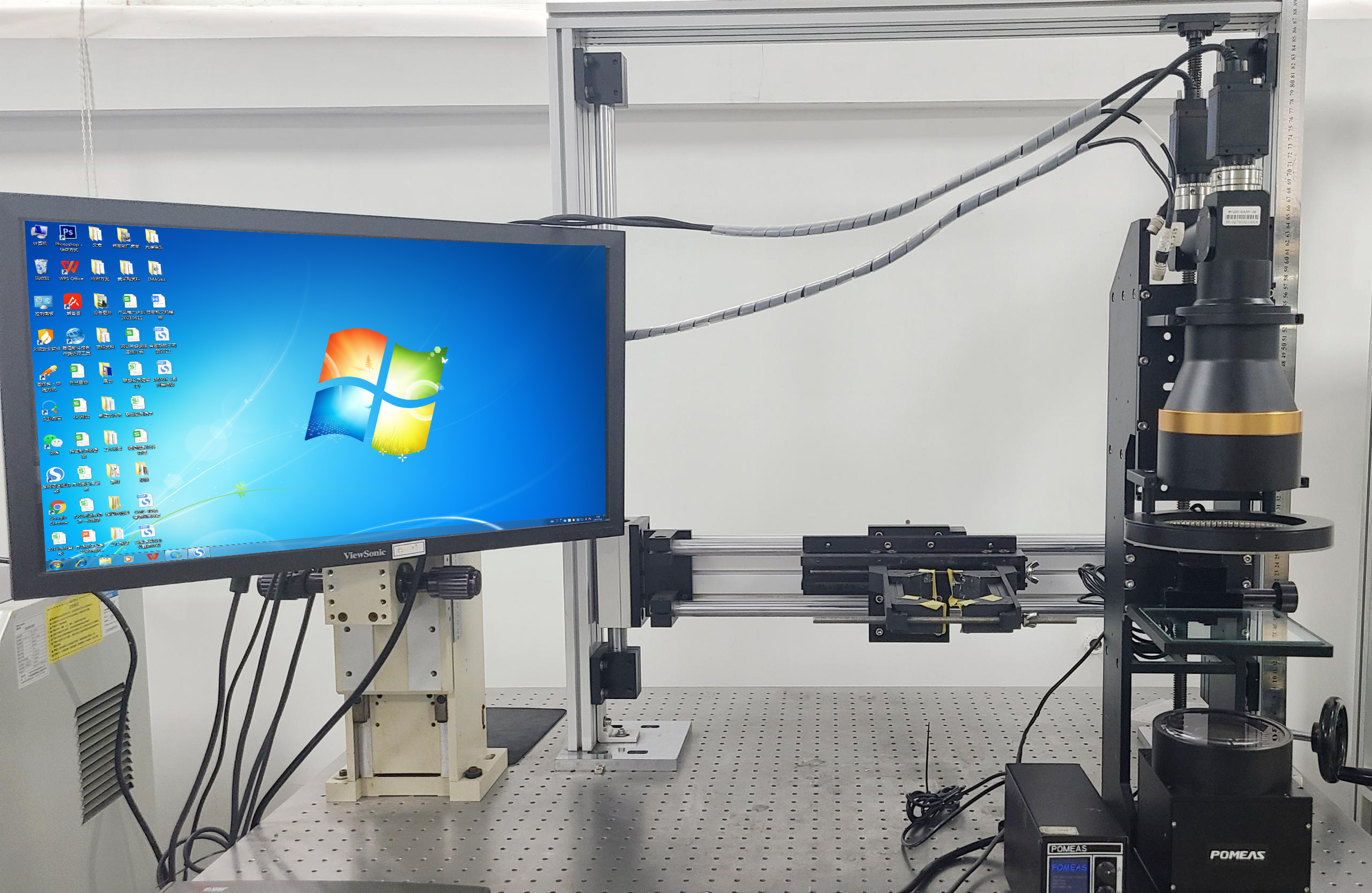
C、Lens to Camera Matching
1. Camera sensor size and the image plane size of the lens: if the image plane size of the lens is smaller than the camera sensor size, there will be dark corners of the image or even can not cover the entire sensor; on the contrary, if the image plane size of the lens is too large, it will result in a waste of resources and may affect the quality of imaging. In general, the image plane size should be selected slightly larger than or equal to the camera sensor size of the lens.

2. Resolution: the resolution of the camera determines the number of image details that can be captured, while the resolution of the lens determines the ability to clearly image the details of the object. If the lens resolution is lower than the camera resolution, even if the camera is able to capture more pixels, but also can not present a clear image; on the contrary, the lens resolution is too high and the camera resolution is not enough, the same can not give play to the performance advantages of the lens. Therefore, in the selection to ensure that the lens and camera resolution match each other to achieve the best imaging results. In addition, it is also necessary to consider whether the frame rate of the camera and the response speed of the lens to match, in the high-speed detection scene, the two must work together in order to accurately capture fast-moving objects.
D、Impact of external conditions: necessary preparation for a complex environment
1. Temperature: In high or low temperature environments, the optical material of the lens may undergo thermal expansion and contraction, resulting in changes in focal length and affecting imaging clarity. Therefore, lenses working in high-temperature environments need to have good high-temperature resistance and select optical materials with high thermal stability; in low-temperature environments, the lens should be considered anti-freezing and insulation measures.
2. Humidity: humid environments are prone to water vapor condensation inside the lens, resulting in moldy, foggy lenses, affecting imaging quality. For lenses used in high humidity environments, products with moisture resistance should be selected, and protective measures such as sealing and drying can also be taken when necessary. In addition, the industrial site of electromagnetic interference, vibration and other factors may also affect the performance and stability of the lens. In an environment with electromagnetic interference, choose lenses with electromagnetic shielding; for scenes with high vibration, you need to equip the lens with a solid mounting bracket and vibration damping device to ensure that the lens remains stable in the work process.
The selection of industrial telecentric lenses is a task that requires comprehensive consideration of multiple inspection needs. Only by fully understanding the suitability of the object under test, determining the appropriate working distance, realizing a good match between the lens and the camera, and fully considering the impact of external conditions, can we select the most suitable industrial telecentric lens for the machine vision program to ensure that the inspection system operates stably and efficiently, and provide strong support for quality control and automation upgrading of industrial production.
Product recommendation
TECHNICAL SOLUTION
MORE+You may also be interested in the following information
FREE CONSULTING SERVICE
Let’s help you to find the right solution for your project!


 ASK POMEAS
ASK POMEAS  PRICE INQUIRY
PRICE INQUIRY  REQUEST DEMO/TEST
REQUEST DEMO/TEST  FREE TRIAL UNIT
FREE TRIAL UNIT  ACCURATE SELECTION
ACCURATE SELECTION  ADDRESS
ADDRESS Tel:+ 86-0769-2266 0867
Tel:+ 86-0769-2266 0867 Fax:+ 86-0769-2266 0867
Fax:+ 86-0769-2266 0867 E-mail:marketing@pomeas.com
E-mail:marketing@pomeas.com
