
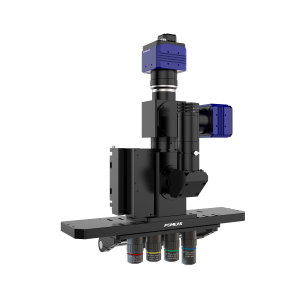
Image autofocus microscope is a high-precision imaging solution integrating optical, mechanical, electronic and algorithmic technologies, which is widely used in scientific research, industrial inspection and precision machining.
I. System Components
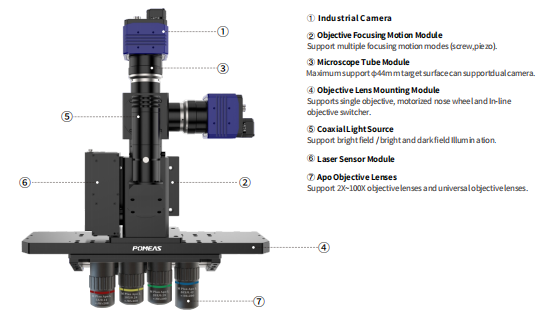
The core modules of the image autofocus microscope system are industrial camera, microscope tube, light source system, objective focusing motion module, laser sensor, objective mounting and APO objective, and the modules work together to achieve stable and efficient focusing and imaging.
1. The industrial camera captures the details of the sample under the microscope and needs to have high resolution (e.g., megapixels), high sensitivity (low noise), and a fast frame rate (for dynamic focusing requirements).
2. The microscope tube connects the objective lens to the camera and adjusts the optical path to match the magnification and working distance of the different objective lenses.
3. The light source system provides uniform, controlled illumination to ensure that the surface features of the sample are clearly visible.
4. Objective focusing motion module adjusts the Z-axis position of the objective lens or sample through a precision motion mechanism to realize fast focusing.
5. The laser sensor monitors the height of the sample surface in real time and feeds back to the control system to drive the focusing module.
6. The objective lens mounting interface has single hole, in-line interface (4 holes), round interface (5 holes), and adopts high rigidity bayonet to ensure the coaxiality of the objective lens and the mirror tube;
7. 2X to 100X APO objective lens can be used to correct the spherical aberration and chromatic aberration of red, blue and green light for clearer imaging.
II. Programmatic Features


1. Static and Dynamic Real-Time Focus
① Support static focus: fixed sample surface (e.g. metal parts detection); support dynamic focus: moving samples or surfaces (e.g. assembly line detection, biological cell dynamic observation).
② Response speed: internal update rate up to 10kHz, output rate 6.5kHz, real-time tracking of high-speed moving samples.
2. High-speed and High-precision Focusing
① Speed: optimized by POMEAS algorithm, short focus adjustment time (milliseconds), adapted to high-speed processing (such as laser cutting);
② Accuracy: micron-level (or even nanometer-level) focusing accuracy, adapting to complex surfaces (e.g. rough metals, diffuse reflective plastics).
3. Easy Integration
① Interface compatibility: supports analog output (voltage/current) and digital output (RS232, USB, Ethernet);
② Controller options: third-party motion systems (stepper motors, linear motors, piezo stages) can be connected to simplify system integration.
4. High Flexibility
① Applicable to a variety of materials: no pattern (homogeneous surface), patterned (such as circuit boards), rough (metal burrs), diffuse reflection (plastics); according to different materials automatically adjust the laser power and sensor gain to adapt to high-light or low-light surfaces.
② Objective lens compatibility: supports 2X to 100X objective lenses, covering low magnification macro observation to high magnification micro analysis.
III. Typical Applications
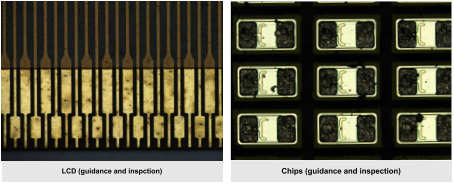
1. Real-time Focusing for Microscopic Observation
① Scenario: biomedicine (cell dynamic observation), material science (nanostructure analysis), semiconductor inspection (chip defect screening);
② Requirements: when the sample surface is uneven or moving (e.g., living cells), the focus needs to be continuously maintained to ensure clear imaging.
2. Precision Laser Processing
① Scenario: laser welding (electronic component connection), laser cutting (sheet metal), laser marking (product traceability);
② Requirements: the distance between the processing head and the material surface needs to be precisely controlled (error <1μm), and automatic focusing avoids false welding or cutting deviation.
3. Industrial Inspection and Automation
① Scenario: 3C product inspection (cell phone screen scratches), PCB board inspection (solder joints), food packaging (label integrity);
② Requirements: high-speed assembly lines, samples move quickly and have diverse surfaces, requiring a combination of dynamic focus and high-precision inspection.
Product recommendation
TECHNICAL SOLUTION
MORE+You may also be interested in the following information
FREE CONSULTING SERVICE
Let’s help you to find the right solution for your project!


 ASK POMEAS
ASK POMEAS  PRICE INQUIRY
PRICE INQUIRY  REQUEST DEMO/TEST
REQUEST DEMO/TEST  FREE TRIAL UNIT
FREE TRIAL UNIT  ACCURATE SELECTION
ACCURATE SELECTION  ADDRESS
ADDRESS Tel:+ 86-0769-2266 0867
Tel:+ 86-0769-2266 0867 Fax:+ 86-0769-2266 0867
Fax:+ 86-0769-2266 0867 E-mail:marketing@pomeas.com
E-mail:marketing@pomeas.com
