
Autofocus technology is a critical function in modern imaging systems, widely applied in microscopes, cameras, medical equipment, and industrial inspection. Its core objective is to intelligently adjust optical systems to produce the sharpest possible image of the observed object on the image sensor. Current mainstream autofocus methods primarily include image analysis-based focus evaluation functions and laser-assisted focusing technology based on active ranging.
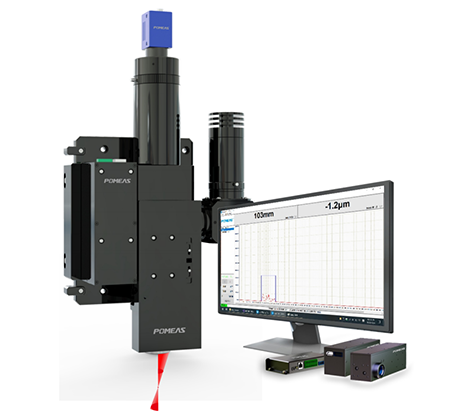


1. Z-Axis Scanning Method Based on Image Clarity Evaluation
A precision motor drives the stage or lens to move along the Z-axis, capturing multiple images at different heights. Each image undergoes evaluation through a specific algorithm, generating a sharpness rating by calculating contrast, gradient information, or frequency domain features. By comparing these values, the system determines the Z-axis position corresponding to the optimal focal plane and controls the motor to move to that location for focusing. This method offers high precision and broad applicability. For instance, motorized zoom autofocus microscopes employ this mechanism, making it suitable for scenarios requiring high image quality, such as biological sample inspection and material analysis.


2. The high-efficiency focusing method employs a laser displacement sensor to achieve active distance measurement
This technology directly calculates the actual distance between the objective lens and the sample surface by emitting a laser beam toward the measured object and receiving its reflected light, utilizing either triangulation or time-of-flight ranging principles. The system rapidly adjusts the Z-axis position based on the distance measurement results, enabling real-time focusing. This method offers fast response times and strong resistance to interference, making it particularly suitable for dynamic observation or scenarios demanding high focusing speed. Typical applications include laser confocal microscopy, which combines optical imaging with point scanning technology to achieve high-resolution three-dimensional reconstruction.


3. Comparative Advantages
(1)Image evaluation methods are suitable for complex surfaces and diverse samples, offering high accuracy but requiring significant computational resources.
(2)Laser ranging offers high speed and is suitable for real-time systems, but its performance may be affected by the optical properties of the target object.
Product recommendation
TECHNICAL SOLUTION
MORE+You may also be interested in the following information
FREE CONSULTING SERVICE
Let’s help you to find the right solution for your project!

- APPICATION CASE
- RESOURCE CENTER
- DOWNLOAD CENTER
SOLUTIONS SUPPORT
- ZOOM LENS SELECTION TOOL
- TELECENTRIC LENS SELECTION TOOL
- FA LENS SELECTION TOOL
- ZOOM RATIO TABLE
- CERTIFIED MODEL
SELECTION TOOL
- WHY POMEAS
- FAQ
- PRIVACY POLICY
- TERMS OF USE
- DELIVERY & RETURN POLICY
CUSTOMER CARE
 ADDRESS
ADDRESS
Add.:No.68, Chongwei Road, Baizhoubian, East district, Dongguan, China, 523000
CONTACT
 Tel:+ 86-0769-2266 0867
Tel:+ 86-0769-2266 0867
 Fax:+ 86-0769-2266 0867
Fax:+ 86-0769-2266 0867
 E-mail:marketing@pomeas.com
E-mail:marketing@pomeas.com

Wechat QR code

 ASK POMEAS
ASK POMEAS  PRICE INQUIRY
PRICE INQUIRY  REQUEST DEMO/TEST
REQUEST DEMO/TEST  FREE TRIAL UNIT
FREE TRIAL UNIT  ACCURATE SELECTION
ACCURATE SELECTION 