What are the differences between double-flange lenses and standard industrial lenses?
I. Optical Principle Differences Between Double-Telecentric Lenses and Standard Industrial Lenses

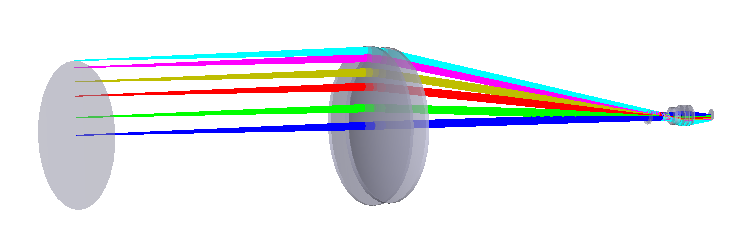
1. The double telecentric lens achieves a dual telecentric structure by placing aperture diaphragms simultaneously on both the object-side and image-side focal planes. Combining the telecentric properties of both sides, it delivers dual stability: changes in object position do not alter magnification, and shifts in camera position do not affect imaging quality.

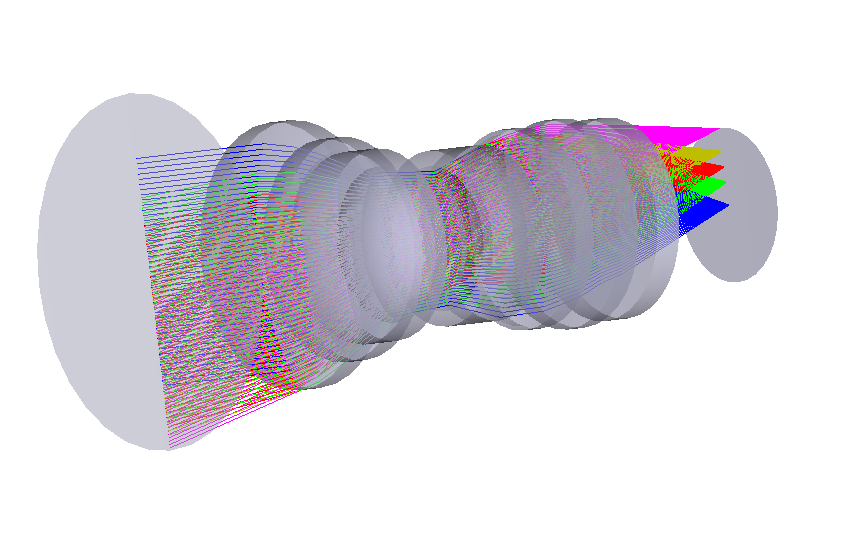
2. Standard Industrial Lens
- Perspective distortion: The farther an object's edge is from the optical axis, the greater the angle of incidence, resulting in the “near large, far small” phenomenon.
- Magnification fluctuation: Image size varies significantly with object distance.
- Limited distortion control: Conventional lenses exhibit higher distortion rates, particularly noticeable in wide-angle or telephoto scenarios.
II. Application Case Comparison


1. Double-telecentric Lens: A precision-engineered “optical ruler”

- Automotive manufacturing sector:
-
Engine Cylinder Block Inspection: Dual telecentric lenses with a 15mm depth of field and AI algorithms calculate cylinder bore wall aperture roundness (accuracy ±0.005mm), flatness (±0.01mm), and positional deviation in real time, resolving local blurring issues caused by insufficient depth of field in traditional lenses.
-
Gear Profile Measurement: A telecentric ZOOM LENS combined with 3D reconstruction technology generates point cloud data for the entire gear tooth surface. Profile measurement error is ≤±0.008mm, surpassing the precision of traditional gear measuring instruments.
-
- Electronic Manufacturing Sector:
- PCB Board Inspection: Dual telecentric lenses with 10mm depth of field support Phase Measurement Profiling (PMP) to capture 3D topography of 0402 resistors and BGA solder joints, achieving coplanarity measurement accuracy of ±0.015mm.
- 5G Connector Inspection: Large-aperture telecentric lenses (supporting a 45.7mm diagonal field of view) paired with a 21-megapixel camera achieve sub-pixel-level pin edge positioning (±0.008mm accuracy) within a 30mm depth of field, while simultaneously detecting pin height variations (±0.02mm).
- PCB Board Inspection: Dual telecentric lenses with 10mm depth of field support Phase Measurement Profiling (PMP) to capture 3D topography of 0402 resistors and BGA solder joints, achieving coplanarity measurement accuracy of ±0.015mm.
2. Standard Industrial Lenses: The Cost-Effective Choice for General Applications

- Production Line Monitoring:
- Part Identification and Positioning: While standard lenses can measure thickness (accuracy ±0.005mm) and edge curvature (±0.01mm) of smartphone glass covers using a 5mm depth of field, they require multiple focus adjustments to cover different height zones. This efficiency falls short of the “one-click flash measurement” capability offered by dual telecentric lenses.
- Object Contour Detection: When inspecting injection mold cavities, standard lenses require segmented imaging due to insufficient depth of field (only 0.5mm). In contrast, dual telecentric lenses achieve full-dimension measurement in a single pass (accuracy ±0.01mm) through their 20mm depth of field.
- Part Identification and Positioning: While standard lenses can measure thickness (accuracy ±0.005mm) and edge curvature (±0.01mm) of smartphone glass covers using a 5mm depth of field, they require multiple focus adjustments to cover different height zones. This efficiency falls short of the “one-click flash measurement” capability offered by dual telecentric lenses.
Telecentric lenses, with their core advantages of constant magnification, low distortion, and high depth of field, have become the preferred choice in high-precision manufacturing. Conventional industrial lenses, characterized by their low cost and broad applicability, dominate general-purpose scenarios.
Product recommendation
TECHNICAL SOLUTION
MORE+You may also be interested in the following information
FREE CONSULTING SERVICE
Let’s help you to find the right solution for your project!


 ASK POMEAS
ASK POMEAS  PRICE INQUIRY
PRICE INQUIRY  REQUEST DEMO/TEST
REQUEST DEMO/TEST  FREE TRIAL UNIT
FREE TRIAL UNIT  ACCURATE SELECTION
ACCURATE SELECTION  ADDRESS
ADDRESS Tel:+ 86-0769-2266 0867
Tel:+ 86-0769-2266 0867 Fax:+ 86-0769-2266 0867
Fax:+ 86-0769-2266 0867 E-mail:marketing@pomeas.com
E-mail:marketing@pomeas.com
