In the fields of microscopic imaging and precision inspection, the performance of optical lenses directly determines imaging quality and operational flexibility. Among these, 0.7x–4.5x continuous zoom lenses have become core components in industrial inspection, biological microscopy, and materials analysis due to their wide magnification range and flexible adjustment capabilities.


I. Technical Principles and Structural Features
The 0.7x–4.5x lens is a continuous zoom lens, whose core design achieves smooth magnification transitions through the precise coordination of multiple lens groups. Compared to traditional fixed-magnification lenses, its advantages include:
1. Stepless Zoom: By rotating the focus knob, magnification can be continuously adjusted within the 0.7x–4.5x range, adapting to objects of varying sizes without lens changes.
2. Coaxial optical path design: Incorporates built-in beam-splitting prisms or mirror assemblies to maintain consistent optical axis alignment during zoom, preventing image shift.
3. Manual Focus Mechanism: Utilizes mechanical threaded drives or gear sets to move lens elements forward/backward, enabling rapid focusing ideal for real-time observation of dynamic scenes.
Typical Application: Integrated microscopes (e.g., stereo microscopes) often incorporate these lenses, allowing users to simultaneously adjust zoom and focus with one hand, significantly enhancing operational efficiency.
II. Core Parameter Analysis
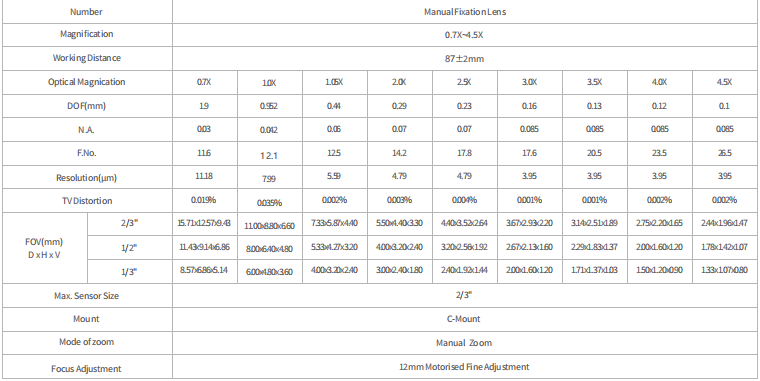
1. Magnification Range and Field of View
Magnification Range: 0.7x to 4.5x covers low-magnification macro observation (e.g., whole-unit inspection) to high-magnification microscopic analysis (e.g., chip pin inspection).
Field of View (FOV) Diameter: Inversely proportional to magnification. Example: On a 2/3-inch sensor (11mm diagonal): At 0.7x magnification, FOV diameter is approximately 1.9mm; at 4.5x magnification, FOV diameter shrinks to 0.1mm.
2. Depth of Field (DOF) Characteristics
DOF decreases sharply with increasing magnification, following the formula: DOF≈NA²/2λN*M²/1 (where λ is wavelength, N is numerical aperture, M is magnification)
Practical performance: At 0.7x magnification, DOF can reach several millimeters, suitable for observing objects with significant surface undulations; At 4.5x magnification, DOF may be only around 0.1mm, requiring strict focus control or depth-of-field extension techniques.
3. Working Distance (WD)
Refers to the distance from the front of the lens to the observed object. For 0.7x–4.5x lenses: WD = 87mm ± 2mm
4. Resolution and Numerical Aperture (NA)
Theoretical resolution: R = NA × 0.61λ (Rayleigh criterion). High NA lenses resolve finer structures but offer shallower depth of field.
Practical performance: For 0.7x–4.5x lenses, NA typically ranges from 0.03 to 0.085, yielding resolution between 1–10μm—sufficient for most industrial inspection requirements.
III. Typical Application Scenarios
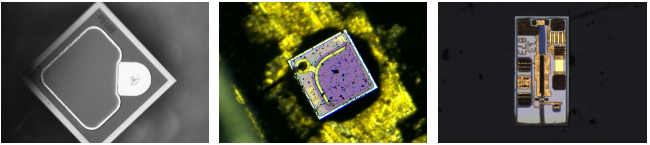
1. Electronics Manufacturing: PCB defect inspection, chip pin coplanarity measurement.
2. Biomedical: Tissue section observation, cell morphology analysis (requires fluorescence module).
3. Materials Science: Metal surface crack detection, coating thickness measurement.
4. Precision Assembly: Micro-part alignment, soldering quality verification.
Product recommendation
TECHNICAL SOLUTION
MORE+You may also be interested in the following information
FREE CONSULTING SERVICE
Let’s help you to find the right solution for your project!


 ASK POMEAS
ASK POMEAS  PRICE INQUIRY
PRICE INQUIRY  REQUEST DEMO/TEST
REQUEST DEMO/TEST  FREE TRIAL UNIT
FREE TRIAL UNIT  ACCURATE SELECTION
ACCURATE SELECTION  ADDRESS
ADDRESS Tel:+ 86-0769-2266 0867
Tel:+ 86-0769-2266 0867 Fax:+ 86-0769-2266 0867
Fax:+ 86-0769-2266 0867 E-mail:marketing@pomeas.com
E-mail:marketing@pomeas.com
